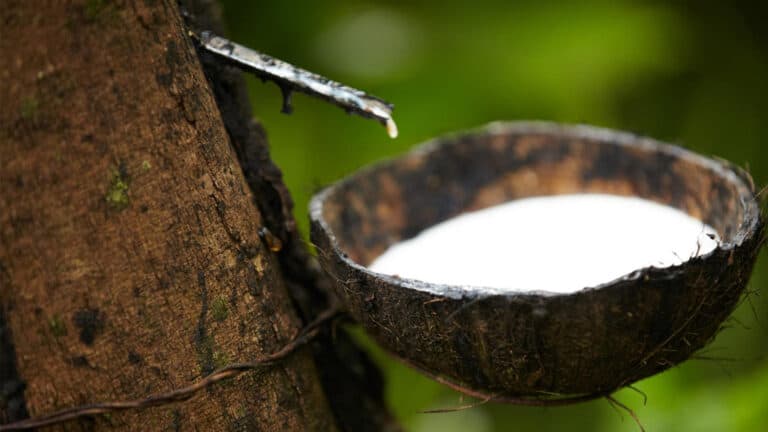
WHAT IS RUBBER? Rubber is an elastic material made from petroleum, natural gas, or natural plant exudates from some tropical plants. Rubber is the primary component of tires for bicycles, cars, and airplanes due to its flexibility, durability, and hardness. TYPES OF RUBBER: There are two main types of rubber, natural rubber, and synthetic rubber: Natural Rubber: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lUg7r7fu_eo These are the naturally occurring elastomers. Natural rubber is created from latex, which falls from the bark of several tropical and subtropical trees. Latex is a milky white liquid that contains solid particles suspended in it. The central locations for this latex rubber are Brazil, India, Indonesia, Malaysia, and Sri Lanka. It is known as cis- 1, 4-polyisoprene and is produced by polymerizing isoprene (2 methyl-1, 3-butadiene), which has the chemical formula (C5H8). In layman’s terms, we may state that they are produced by forming a lengthy, tangled chain by loosely fusing the isoprene (C5H8) monomers together. Manufacturing Process of Natural Rubber: The collection of latex from rubber trees is the first step in the manufacture of natural rubber. The first step in collecting latex from rubber trees is to score or cut into the tree’s bark. Latex pours into a cup that is fastened to the base of the tree’s cut. Large tanks are used to collect the latex material from several trees. Coagulation, a procedure that thickens or curdles polyisoprene into a mass, is the most typical way to separate the rubber from latex. The latex is treated in this way by adding an acid, such as formic acid. It takes the coagulation process roughly 12 hours. The rubber’s coagulum is pressed dry using a succession of rollers. In smokehouses, the resulting thin sheets—which are roughly 1/8 inch thick—are dried on wooden racks. In most cases, drying takes several days. The resulting ribbed smoke sheet, a dark-brown rubber, is then bundled into bales and transported to the processor. But not all rubber is smoked. An air-dried sheet of rubber is one that has been dried without the use of smoke. Better rubber is produced as a result of this technique. Pale crepe rubber, which is an even higher grade rubber, needs to go through two coagulation processes before being allowed to air dry. Synthetic Rubber: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=x7ehv8dSHYQ&t=3s Petroleum and natural gas are used in the production of synthetic rubbers. It can be made by copolymerizing 1, 3-butadiene with an unsaturated monomer or by polymerizing 1, 3-butadiene derivatives. Manufacturing Process of Synthetic Rubber: Over the years, numerous varieties of synthetic rubber have been created. All are the end product of molecular joining or polymerization. Molecules are linked together to form lengthy chains through a process known as addition polymerization. As molecules are joined together, another process known as condensation polymerization removes a piece of the molecule. Examples of other polymers include styrene butadiene rubber (SBR), which is used as the non-bounce rubber in tires, and synthetic rubbers manufactured from polychloroprene (neoprene rubber), an oil- and gasoline-resistant rubber. During World War I, the first significant quest for synthetic rubber started in Germany. Germany was unable to obtain natural rubber due to British blockades. German chemists created the polymer [CH2=C(CH3)C(CH3)=CH2] from acetone using 3-methyl isoprene (2,3-dimethyl-1,3-butadiene) units. By the end of World War I, Germany was producing 15 tons per month of methyl rubber, despite the fact that it was inferior to natural rubber. Better synthetic rubbers are now available thanks to continued development. Buna S (styrene butadiene rubber, or SBR), the most popular kind of synthetic rubber currently in use, was created in 1929 by the German business I.G. Farben. An artificial rubber-like polymer made up of 98 percent cis-1,4-polyisoprene was created in 1955 by American chemist Samuel Emmett Horne, Jr. Since 1961, tires have been made with this material and SBR. Rubber Preparation: Rubber tapping: By making a small V-cut in the tree bark, the milky white liquid latex from the rubber trees is collected in a cup. To coagulate the rubber particles, the collected latex is cleaned, filtered, and acid-reacted. Mastication: The rubber that was acquired during the tapping process is still not ready for use. It has a very brittle character while cold and becomes quite gluey when warmed up. The rubber is squeezed and let to travel through the rollers to make it softer and more workable, eliminating its brittleness and pungent smell. Depending on the qualities needed for the rubber, this process is repeated. To improve the qualities of rubber, additional chemical compounds are also added throughout this procedure. Calendering is a procedure that is mostly used to give the rubber shape utilizing rollers (after proper mixing of the chemical ingredients). Using an extrusion machine with specifically shaped perforations, the final product is then extruded to create hollow tubes. The process of vulcanization is necessary to produce rubber that is durable and strong enough to be employed in machinery and goods like vehicle tires. Sulfur is added to the rubber and heated at a temperature between 373 K and 415 K to improve all of these characteristics. Vulcanization is the term for this process. After vulcanization, the sulfur works as a cross-linking agent, causing the rubber to become cross-linked and rigid. ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT OF RUBBER PRODUCTION: The production of natural rubber is utilized in the tire industry to a degree of around 70%. An assessment of the natural rubber production process reveals that the environmental effects are related to forest clearing, the use of energy, chemicals, fertilizers, and biocides, as well as emissions into the water. Sources: Natural Rubber and Synthetic Rubber – Examples, Preparation, Properties, Uses and FAQs of Natural and Synthetic Rubber. (2019, December 25). BYJUS; byjus.com. https://byjus.com/chemistry/natural-rubber-and-properties/ The Manufacturing Process of Rubber. (2018, December 15). Sciencing; sciencing.com. https://sciencing.com/manufacturing-process-rubber-5206099.html By Hassan Nasser, 23 August 2022. How Is Rubber Made? WHAT IS RUBBER? Rubber is an elastic material made from petroleum, natural gas, or natural plant exudates… Natural Rubber Shortage: A Crisis at the Gates Natural rubber with all its chemical and physical properties is